Schwan, Leanne
Page Navigation
- Home
-
Global 10
- 10.1 The World in 1750 C.E.
- 10.2 Enlightenment, Revolution, and Nationalism
- 10.3 Causes and Effects of the Industrial Revolution
- 10.4 Imperialism
- 10.5 Unresolved Global Conflict (1914-1945)
- 10.6 Unresolved Global Conflict (1945-1991)
- 10.7 Decolonization and Nationalism
- 10.8 Tensions Between Cultural Traditions and Modernization
- 10.9 Tensions Between Cultural Traditions and Modernization
- 10.10 Human Rights Violations
- 9.1/10.0 Historical Thinking
-
Global 9
- 9.1/10.0 Historical Thinking
- 9.2 - The First Civilizations
- 9.3 Classical Civilizations
- 9.4 Political Powers and Achievements
- 9.5 Social and Cultural Growth and Conflict
- 9.6: Ottoman and Ming Pre-1600
- 9.7: Transformation of Western Europe and Russia
- 9.8: Africa and the Americas Pre-1600
- 9.9: Interactions and Disruptions
- Global Resources
- Global Review
- HMH TEXTBOOK PDF
- SUB PLANS
- CL Foundations in Education - IONA
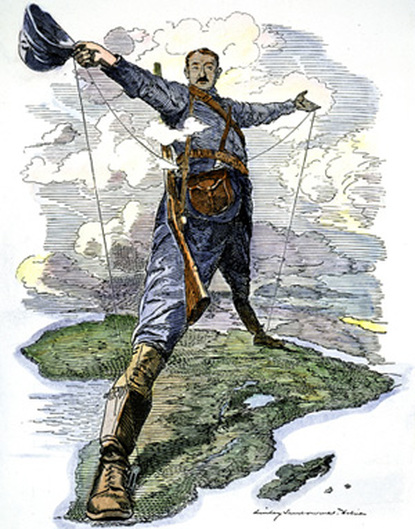
10.4 Imperialism

-
ESSENTIAL QUESTION:
Why did nations choose to colonize others and how did this choice impact the world?
Unit Essential Question:
- How do turning points change history?
-
10.4 Brainpop Videos
- British Empire
-
IMPERIALISM: Western European interactions with Africa and Asia shifted from limited regional contacts along the coast to greater influence and connections throughout these regions. Competing industrialized states sought to control and transport raw materials and create new markets across the world.
(Standards: 2, 3, 4; Themes: MOV, TCC, GEO, GOV, EXCH)