Schwan, Leanne
Page Navigation
- Home
-
Global 10
- 10.1 The World in 1750 C.E.
- 10.2 Enlightenment, Revolution, and Nationalism
- 10.3 Causes and Effects of the Industrial Revolution
- 10.4 Imperialism
- 10.5 Unresolved Global Conflict (1914-1945)
- 10.6 Unresolved Global Conflict (1945-1991)
- 10.7 Decolonization and Nationalism
- 10.8 Tensions Between Cultural Traditions and Modernization
- 10.9 Tensions Between Cultural Traditions and Modernization
- 10.10 Human Rights Violations
- 9.1/10.0 Historical Thinking
-
Global 9
- 9.1/10.0 Historical Thinking
- 9.2 - The First Civilizations
- 9.3 Classical Civilizations
- 9.4 Political Powers and Achievements
- 9.5 Social and Cultural Growth and Conflict
- 9.6: Ottoman and Ming Pre-1600
- 9.7: Transformation of Western Europe and Russia
- 9.8: Africa and the Americas Pre-1600
- 9.9: Interactions and Disruptions
- Global Resources
- Global Review
- HMH TEXTBOOK PDF
- SUB PLANS
- CL Foundations in Education - IONA
10.2 Enlightenment, Revolution, and Nationalism

PPT 10.02 Enlightenment, Revolution, Nationalism
-
Unit Essential Question:
- How do turning points change history?
ESSENTIAL QUESTION:
How did new ideas spark change and conflict in the late 18th and throughout the 19th centuries?
-
10.2 Brainpop Videos
- French Revolution
- Napoleon Bonaparte
- Simon Bolivar
- Haitian Revolution
-
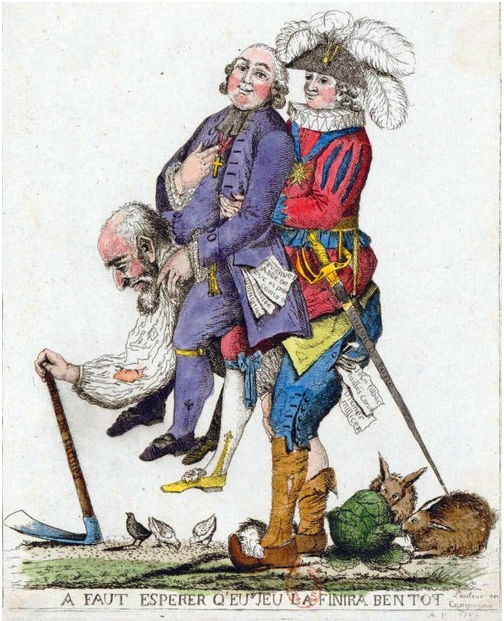
ENLIGHTENMENT, REVOLUTION, AND NATIONALISM: The Enlightenment called into question traditional beliefs and inspired widespread political, economic, and social change. This intellectual movement was used to challenge political authorities in Europe and colonial rule in the Americas. These ideals inspired political and social movements.
(Standards: 2, 3, 5; Themes: MOV, TCC, GEO, SOC, GOV, CIV)

Chapter Review
Videos
-

French Revolution - Storming of the Bastille
French Revolution - Storming of the Bastille and the October Days.mp4 82.1 MB (Last Modified on March 2, 2020)